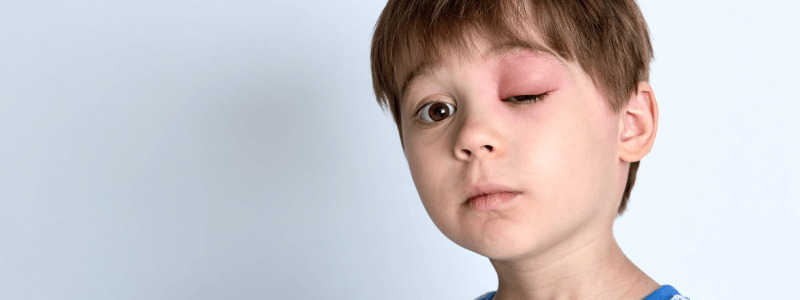
An 11-year-old boy presents with a painful, red, swollen left eye. He has had a recent sinus infection but has no other medical history of note. His temperature is 38.2°C. His eye movements are painful, and he is complaining of double vision.
Show Answer
This patient has a diagnosis of orbital cellulitis. Orbital cellulitis is a medical emergency and occurs when there is infection of the eye tissues posterior to the orbital septum.
2. What is the principal differential diagnosis, and how can the two diagnoses be distinguished?
Show Answer
The principal differential diagnosis is peri-orbital cellulitis. Peri-orbital (or pre-septal) cellulitis is an infection of the eyelid and skin around the eye anterior to the orbital septal.
Peri-orbital cellulitis can present with the following features:
- Eyelid swelling
- Erythema around the eye
- Discharge
- Closure of the eye
- Conjunctival injection
- Fever (generally mild)
- Teary eyes
Orbital cellulitis can be distinguished from peri-orbital cellulitis by the presence of any of the following features:
- Painful eye movements
- Proptosis
- Red desaturation
- Loss of vision
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Diplopia
- Optic neuropathy
Show Answer
The commonest causative organisms are:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Haemophilus influenzae
Header image used on licence from Shutterstock





Excellent, quick short learning activity.