
Thyroid Storm
Thyroid storm, also known as thyrotoxic crisis, is a rare but life-threatening condition characterised by an extreme exacerbation of thyrotoxicosis symptoms. It occurs in approximately 1-2% of patients with established hyperthyroidism. This medical emergency demands...
Antifreeze Poisoning
Ethylene glycol, a component commonly found in antifreeze, presents a serious toxicological emergency. Though it initially acts like ethanol, its metabolism leads to highly toxic acid by-products, resulting in multiorgan damage if not recognised and treated early....
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions are exaggerated or inappropriate immunologic responses occurring in response to an antigen or allergen. Gell and Coombs described four classes in 1963: Type I hypersensitivity reactions Type II hypersensitivity reactions Type III...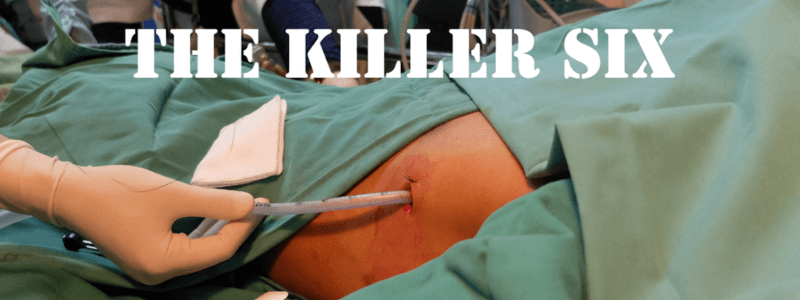
Life Threatening Chest Injuries in Trauma – The Killer Six
Trauma remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with chest injuries representing a significant portion of these cases. Whether resulting from motor vehicle accidents, falls, or penetrating trauma, injuries to the chest can lead to immediate compromise of vital...




