

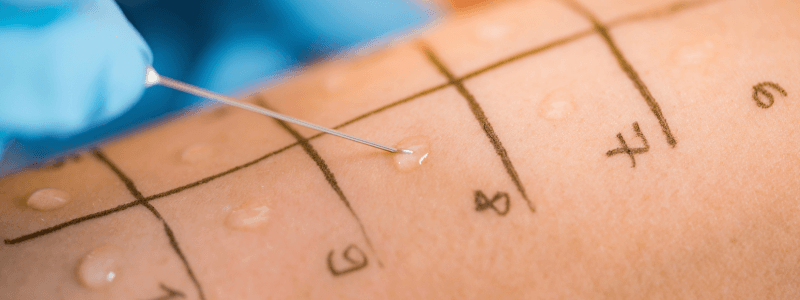
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions are exaggerated or inappropriate immunologic responses occurring in response to an antigen or allergen. Gell and Coombs described four classes in 1963: Type I hypersensitivity reactions Type II hypersensitivity reactions Type III...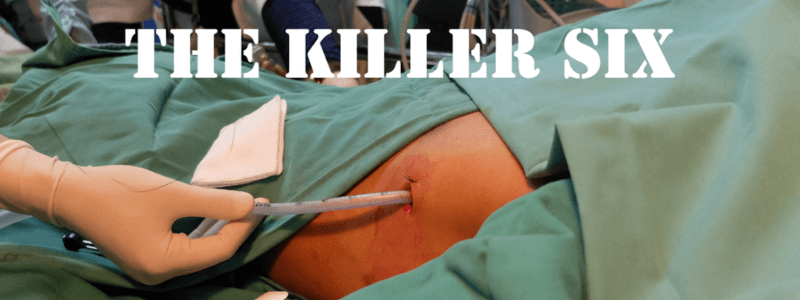
Life Threatening Chest Injuries in Trauma – The Killer Six
Trauma remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with chest injuries representing a significant portion of these cases. Whether resulting from motor vehicle accidents, falls, or penetrating trauma, injuries to the chest can lead to immediate compromise of vital...
What Killed George Washington?
George Washington is undoubtedly one of the world’s most famous historical figures. He served as the Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army during the American War of Independence, presided over the 1787 convention that drafted the United States...
Methaemoglobinaemia
Methaemoglobinaemia occurs when red blood cells contain methaemoglobin at levels higher than 1%. Methaemoglobinaemia results from the presence of iron in the ferric form instead of the usual ferrous form. The ferric form is unable to bind oxygen, and its presence...




