


Practice Questions for the MRCEM Primary Exam
The MRCEM Primary is a daunting and notoriously difficult prospect and also represents the first step towards achieving a training post in Emergency Medicine and ultimately entering the Specialist Register. The MRCEM Primary examination is sat twice yearly. The paper...
Common Antidotes Used in Toxicology
An antidote is an agent that counteracts the effects of a poison, toxin, or harmful substance on the body. They are specifically designed to neutralise or reverse the toxic effects caused by the substance, mitigating or preventing further harm and promoting...
Confounding, Bias and Effect Modification
Confounding factors A confounding factor is a variable that is associated with both the outcome of interest and the exposure of interest. In this constellation, the exposure of interest appears (spuriously) to be associated with the outcome of interest, while in...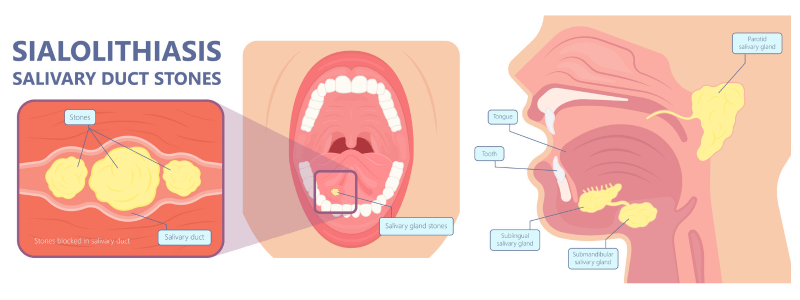
Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis is a condition where a calcified stone (sialolith) forms within a salivary gland. The salivary glands The salivary glands are exocrine glands that produce saliva and secrete it into the oral cavity. There are three main salivary glands and...




