
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
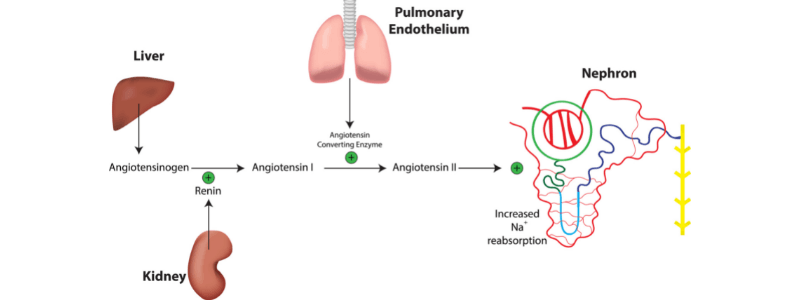
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormonal system that is responsible for the regulation of arterial blood pressure and of the concentration of sodium in the plasma. Renin and angiotensinogen The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the...
Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease (primary adrenal insufficiency) is caused by the underproduction of the steroid hormones by the adrenal glands. Glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid and sex steroid production are all affected. It is more common in women than in men and most commonly...
Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism occurs when there are excessive circulating levels of aldosterone. Hyperaldosteronism can be subdivided into two main types: Primary hyperaldosteronism (~95% of cases) Secondary hyperaldosteronism (~5% of cases) Primary hyperaldosteronism is...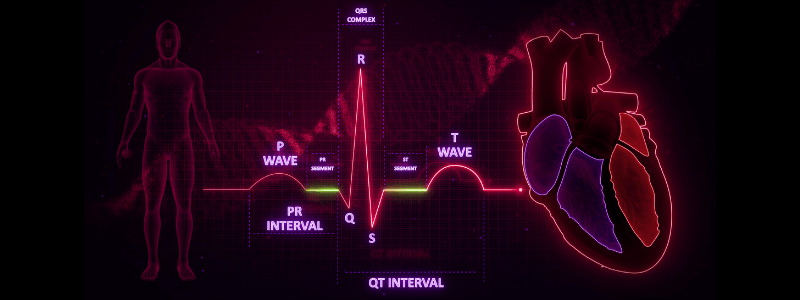
Test Your ECG Knowledge – Waves, Segments and Intervals
Test your knowledge of the ECG waves, segments and intervals with these questions. 1. Which single statement regarding the p wave on the ECG is true? A. It is normally between 120 and 150 ms in duration B. It is positive in lead AVR C. It represents atrial...