

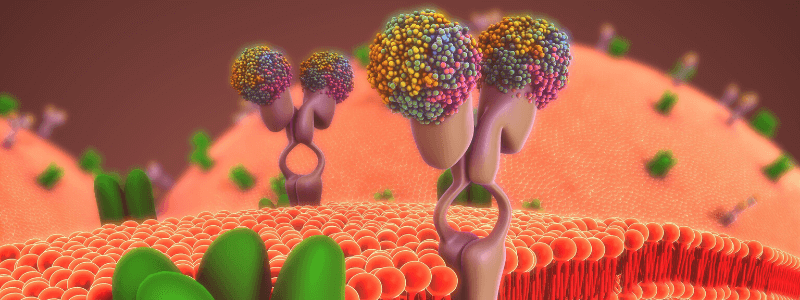
Cell Structure and Function Part 2 – The Cell Membrane
In Part 1 of our ‘Cell Structure and Function’ series we learnt about basic cell structure and the organelles. We now move on to the cell membrane and membrane transport. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, physically separates the inside of the cell...
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 – The Organelles
The cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, it is the functional and structural unit of all living things and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. The human body contains several billion cells, encompassing a vast range of types...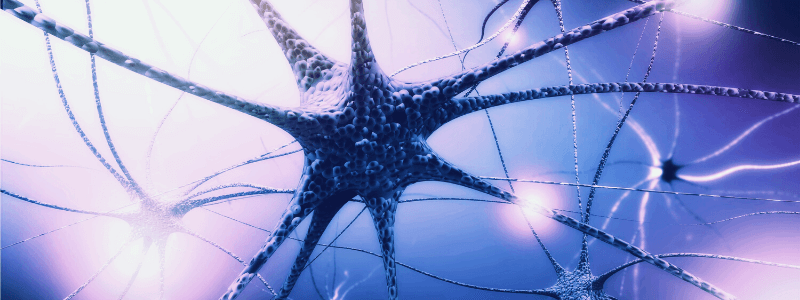
Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands. It acts to regulate numerous body processes, such as blood pressure and respiratory rate, acting as the effector component of homeostasis. The...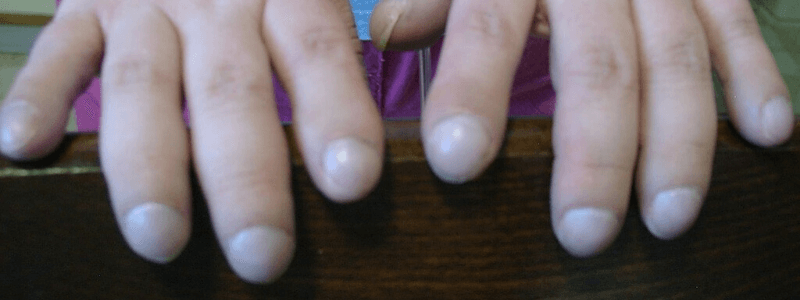
Digital Clubbing
Digital clubbing is one of the oldest recognised signs in medicine, first formally documented by Hippocrates nearly 2500 years ago. For this reason, it is also known as “Hippocratic fingers”. It is an important clinical sign that can assist in the...




