Exam Tips
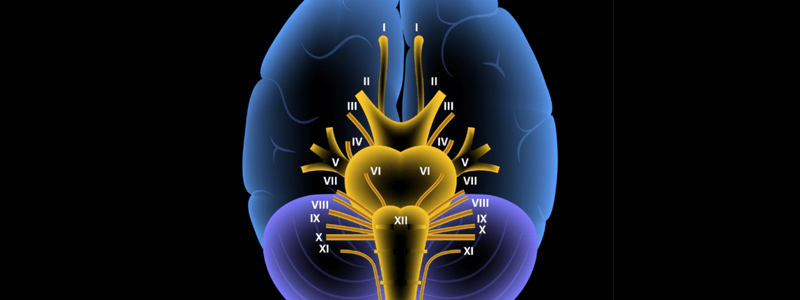
Overview of the Cranial Nerves
There are twelve paired cranial nerves in total, and they all arise directly from the brain, in contrast to the spinal nerves, which arise from segments of the spinal cord. The cranial nerves are accordingly numbered by the location within the brainstem (superior to...

Understanding Vivas
“The spoken word was the first technology by which man was able to let go of his environment in order to grasp it in a new way.” Marshall McLuhan The dreaded viva voce The viva voce, or oral exam, has declined in popularity over recent years but is still a part of...
Understanding Medical Acronyms and Abbreviations
“brb, ttyl ok? Wow, I saved a ‘ton’ of time with those acronyms.” – Stephen Colbert Acronyms are abbreviations formed from the initial components in a phrase or a word. These are usually presented are individual letters. These acronyms are very commonplace in...
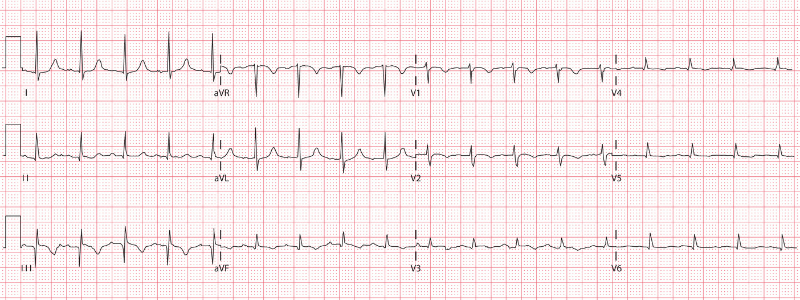
Recognising Myocardial Infarction Patterns on the ECG
Being able to rapidly identify an acute myocardial infarction (MI) pattern on the ECG is a vitally important skill for clinicians, particularly those that work front line in the Emergency Department. MI causes permanent damage to heart muscle and any delay in...

Phases of Clinical Research
Bringing new drugs onto the market The process of bringing new drugs (or other health interventions) onto the market is long and arduous and, in some cases, can take years or even decades. Developing any new drug begins by developing an understanding of the disease or...
Lung Volumes and Capacities
Lung volumes, which are also known as respiratory volumes, refer to the various volumes of gas in the lungs at any given time during the respiratory cycle. Lung capacities are derived from a summation of different lung volumes. It is important to have an understanding...
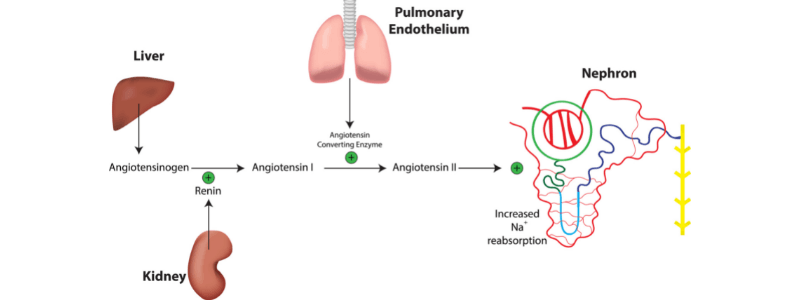
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormonal system that is responsible for the regulation of arterial blood pressure and of the concentration of sodium in the plasma. Renin and angiotensinogen The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the...

Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease (primary adrenal insufficiency) is caused by the underproduction of the steroid hormones by the adrenal glands. Glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid and sex steroid production are all affected. It is more common in women than in men and most commonly...
Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism occurs when there are excessive circulating levels of aldosterone. Hyperaldosteronism can be subdivided into two main types: Primary hyperaldosteronism (~95% of cases) Secondary hyperaldosteronism (~5% of cases) Primary hyperaldosteronism is...
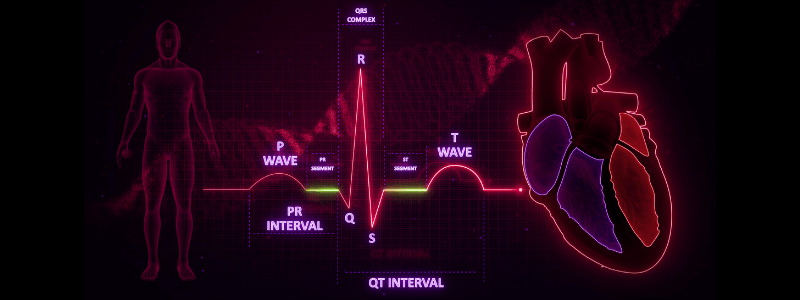
Test Your ECG Knowledge – Waves, Segments and Intervals
Test your knowledge of the ECG waves, segments and intervals with these questions. 1. Which single statement regarding the p wave on the ECG is true? A. It is normally between 120 and 150 ms in duration B. It is positive in lead AVR C. It represents atrial...




