Test your knowledge of pelvic anatomy with these questions.
1. Which of the following is a posterior relation of the vagina?
A. Bladder
B. Urethra
C. Pouch of Douglas
D. Ureter
E. Urogenital diaphragm
Show Answer
Answer: C. Pouch of Douglas
The main relations of the vagina are summarized in the table below:
| Anterior relations | Bladder Urethra |
| Posterior relations | Ampulla of rectum Anal canal Pouch of Douglas Perineal body |
| Lateral relations | Ureter Uterine artery Levator ani Urogenital diaphragm |
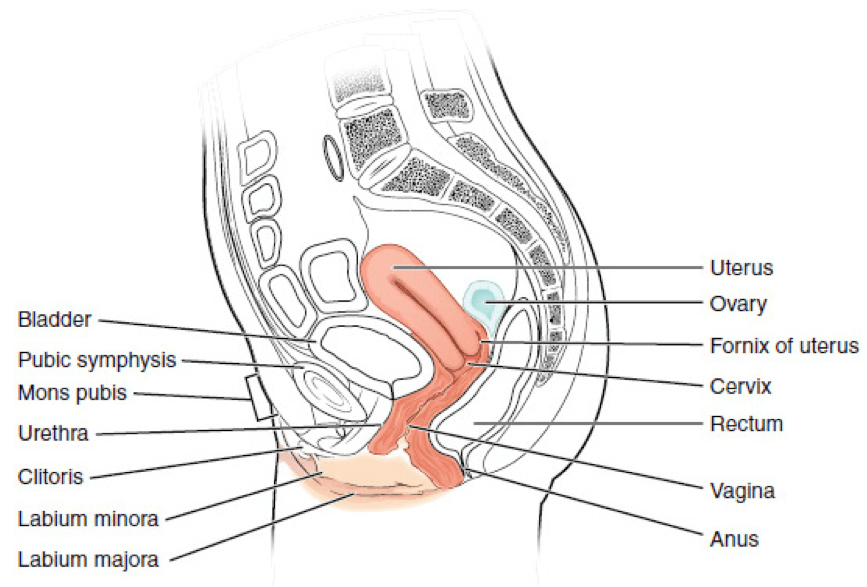
Image sourced from Wikipedia
Courtesy of Carl Fredrik CC BY-SA 3.0
2. The bulbourethral glands open into which part of the male urethra?
A. Navicular fossa
B. Pre-prostatic part
C. Prostatic part
D. Membranous part
E. Spongy part
Show Answer
Answer: E. Spongy part
The urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus. It is approximately 15-20 cm long. In the male it is responsible for the transport of urine and semen out of the body.
There are three points of constriction in the male urethra:
- Internal urethral sphincter
- External urethral sphincter
- External urethral orifice
The urethra can be divided into four parts:
- Pre-prostatic part
- Prostatic part
- Membranous part
- Spongy part
The following table summarises each of these parts:
| Part of urethra | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-prostatic | The intramural part of the urethra. Runs from the internal urethral orifice through the wall of the bladder, and ends at the prostate. |
| Prostatic | The part that passes through the prostate gland. This is the widest and most dilatable part of the urethra. It ends by piercing the urogenital diaphragm. The prostatic part has the following openings that drain into the urethra: • Ejaculatory duct • Prostatic ducts |
| Membranous | The part that passes through the external urethral sphincter. This is the narrowest part of the urethra and is located in the deep perineal pouch. |
| Spongy (penile) | This is the part that passes through the length of the penis. It is the longest part (approx 15 cm in length) and passes through the bulb and corpus spongiosum of the penis. It dilates within the glands penis to form the navicular fossa. The urethra gently curves anteriorly here, before ending at the external urethral orifice. The spongy part contains the opening of bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands) posteriorly. |
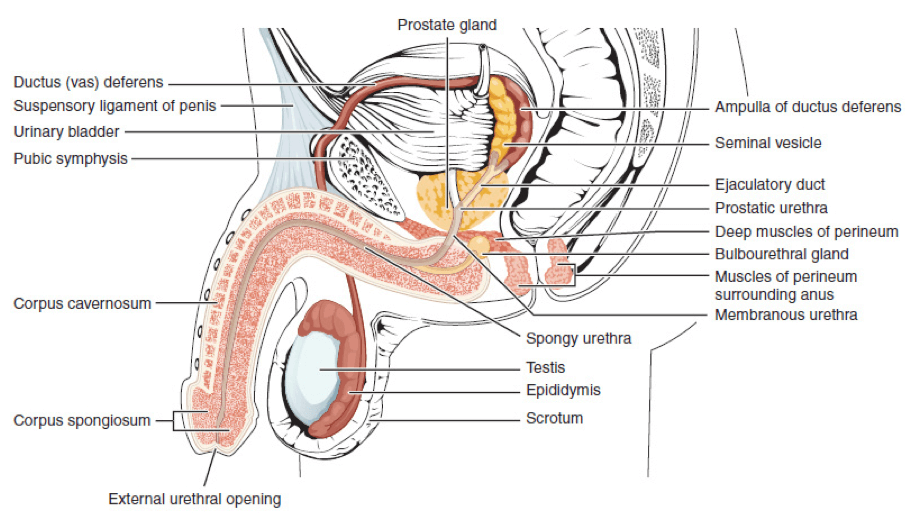
Image sourced from Wikipedia
Courtesy of Carl Fredrik CC BY-SA 3.0
3. Which of the following is a posterior relation of the prostate gland?
A. Neck of the bladder
B. External urethral sphincter
C. Denonvillier’s fascia
D. Levator ani muscle
E. Levator ani muscle
Show Answer
Answer: C. Denonvillier’s fascia
The principal relations of the prostate gland are summarised in the table below:
| Superior relations | Neck of the bladder |
|---|---|
| Inferior relations | External urethral sphincter |
| Anterior relations | Retropubic space Prostatic venous plexuses Puboprostatic ligament |
| Posterior relations | Rectovesical fascia (Denonvillier’s fascia) Ampulla of the rectum |
| Lateral relations | Pelvic floor Levator ani |
4. Sympathetic innervation of the detrusor muscle is via which of the following?
A. Pudendal nerve
B. Hypogastric nerve
C. Inferior mesenteric nerve
D. Pelvic splanchnic nerves
E. Superior mesenteric nerve
Show Answer
Answer: B. Hypogastric nerve
The wall of the urinary bladder contains specialised smooth muscle, the detrusor muscle (detrusor urinae muscle).
The fibres of the detrusor muscle are orientated in three directions and this enables it to retain its structural integrity when stretched. In its relaxed state the detrusor muscle allows the bladder to store urine. During micturition the detrusor muscle contracts.
It receives innervation from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system:
- Sympathetic innervation is via the hypogastric nerve (T12-L2). Sympathetic stimulation causes relaxation of the detrusor muscle and facilitates retention of urine.
- Parasympathetic innervation is via the pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4). Parasympathetic stimulation causes contraction of the detrusor muscle and stimulates micturition.
5. Which SINGLE statement regarding the blood supply of the ovaries is true?
A. The ovarian arteries are branches of the renal arteries
B. The left ovary is supplied by the left renal artery
C. The right ovarian vein drains into the common iliac vein
D. The left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein
E. Both ovarian veins drain directly into the inferior vena cava
Show Answer
Answer: D. The left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein
The arterial supply to the ovaries is from the ovarian arteries, which are direct branches from the abdominal aorta.
Venous drainage from the ovaries is via the ovarian veins. The left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein, whilst the right ovarian vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
For thousands more anatomy tutorials and questions visit: www.anatomyprep.co.uk
Header image used on licence from Shutterstock.