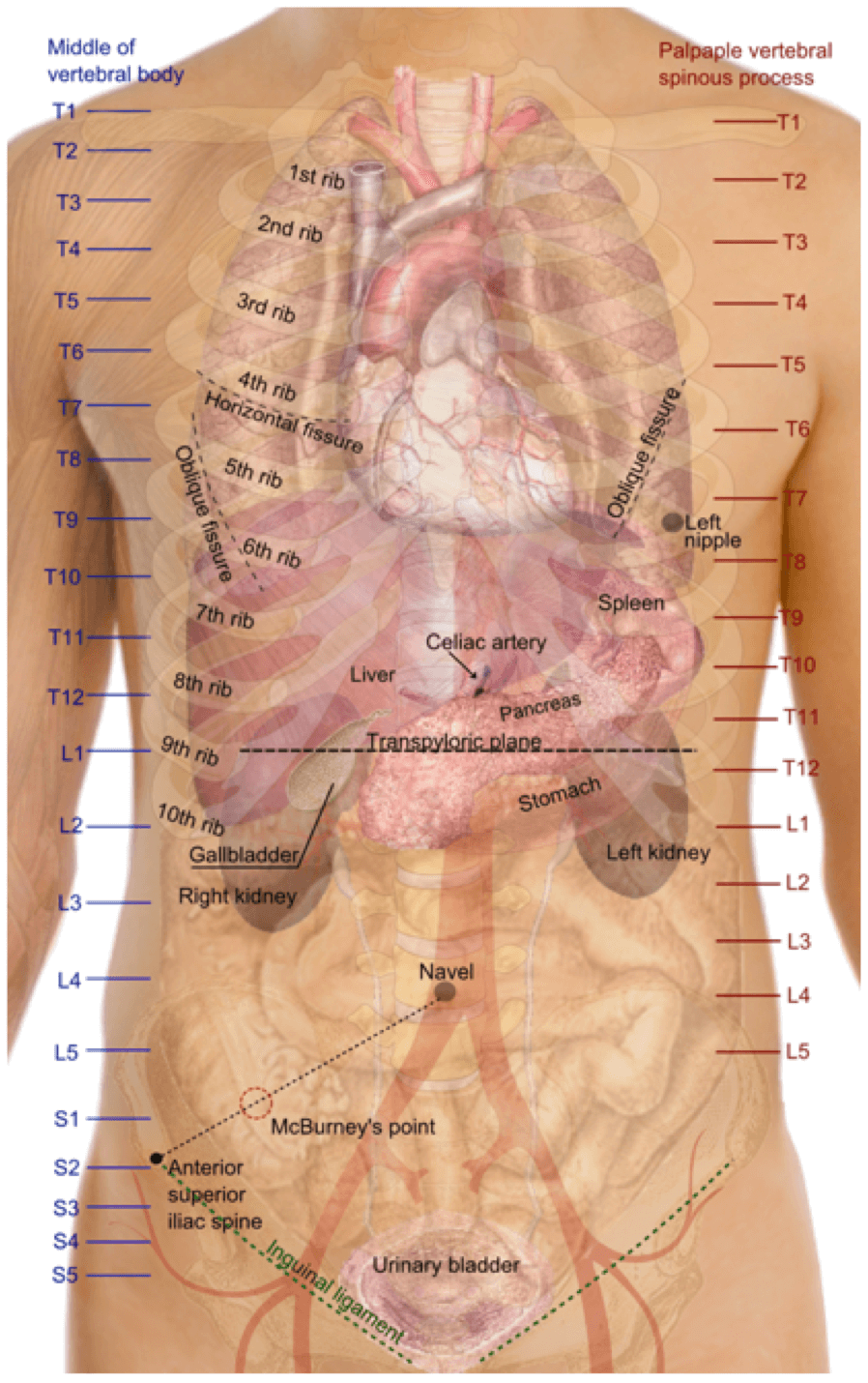
Vertebral levels are very commonly tested on in both undergraduate and postgraduate medical examinations. The most commonly encountered landmarks and structures found at the various vertebral levels are shown in the table below:
| VERTEBRAL LEVEL | LANDMARKS & STRUCTURES |
|---|---|
| C1 | Spinal root of accessory nerve crosses transverse process of atlas |
| C2 | Superior cervical ganglion |
| C3 | Body of hyoid bone |
| C4 | Superior border of thyroid cartilage Bifurcation of common carotid arteries |
| C6 | Cricoid cartilage Larynx ends and trachea begins Pharynx ends and oesophagus begins Inferior thyroid artery crosses carotid sheath Inferior laryngeal nerve enters larynx Vertebral artery enters transverse foramen of C6 Middle cervical ganglion |
| C7 | Vertebra prominens Stellate ganglion Isthmus of thyroid gland |
| T1 | Sternoclavicular joint Highest point of lung apex |
| T2 | Superior border of scapula |
| T2/3 | Suprasternal notch |
| T3 | Medial end of spine of scapula End of oblique fissure of lung posteriorly |
| T3/4 | Top of arch of aorta |
| T3-T4 | Manubrium sterni |
| T4/5 | Sternal angle (of Louis) Bifurcation of trachea Arch of aorta begins and ends Azygous vein enters superior vena cava |
| T5-8 | Body of sternum |
| T6 | Upper border of liver |
| T7 | Inferior angle of the scapula |
| T8 | Caval opening in the diaphragm Phrenic nerves traverse diaphragm |
| T8/9 | Xiphisternal junction |
| T9 | Xiphoid Superior epigastric vessels traverse diaphragm |
| T9-L3 | Costal margin |
| T10 | Oesphageal opening in the diaphragm |
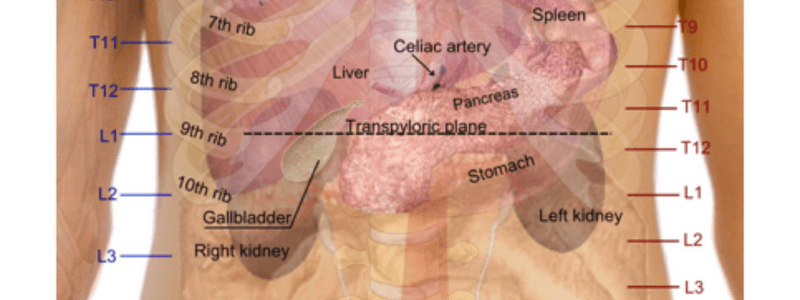
| T12 | Aortic opening in diaphragm Origin of the coeliac axis (lower border) |
| L1 | Transpyloric plane of Addison Fundus of the gallbladder Hila of the kidneys First part of the duodenum Neck of the pancreas Origin of the superior mesenteric artery Origin of the portal vein Pylorus of the stomach Hilum of the spleen Cisterna chyli |
| L1/2 | Spinal cord ends in adults Origin of renal arteries |
| L2 | Subcostal plane Thoracic duct begins Azygous and hemiazygous veins begin Duodenojejunal flexure Ligament of Treitz (upper border) |
| L3 | Origin of inferior mesenteric artery Spinal cord ends in infants |
| L3/4 | Umbilicus |
| L4 | Transtubercular plane Bifurcation of the aorta |
| L5 | Formation of the inferior vena cava |
| S2 | Sacral dimples Midpoint of sacro-iliac joints Posterior superior iliac spines Dural sac ends |
| S3 | Pelvic colon ends and rectum begins Posterior inferior iliac spines |
| S4 | Sacral hiatus Vertebral column ends |
Surface Anatomy Map
Medical Exam Prep would like to thank Dr. Marc Barton for permission to reproduce this extract from his book ‘Essential Clinical Surface Anatomy’.
About Dr. Marc Barton
Dr. Marc Barton qualified from Imperial College School of Medicine in 2001. Since that time he has worked in a variety of different medical specialities. He worked as a GP partner from 2006 until 2008 and more recently as a higher specialist trainee in Emergency Medicine.
‘Essential Clinical Surface Anatomy’ is available for purchase here.






I love the attention to detail and I’m going to order it right now. Dr. Hull, MD